- Surface layer
of work-piece only can be heated by electro-magnetic
induction.
- High surface
hardness, wear resistance and high fatigue limit can
be obtained
- Compressive
residual stress generated by induction hardening brings
superior fatigue limit.
- Process following
heat-treatment can be omitted because of little decarburization
or scaling of work piece.
- Quick and economical
for small lot production is available.
|
|
|
Quenching
spline part of shaft
|
| Facilities
INDUCTION HARDENING |

|
 |
MADE
BY TOCCO(USA)
10KHz 150KW
&O slash;300x2,000 Max
CASE DEPTH 1~5 mm. |
MADE
BY DENSHIKAGAKU (JAPAN
200KHz 40KW
Ø 50x600 Max
CASE DEPTH 0.4 ~ 2.5 mm. |
| HARDNESS
& RESIDUAL STRESS |
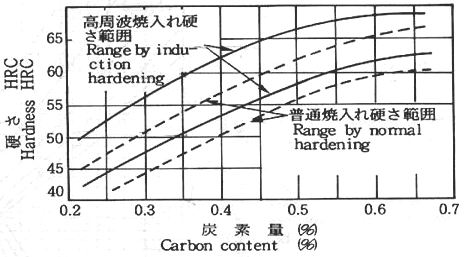
- Quenching hardness
depends on carbon content of material not on hardenability
of it.
- Hardness obtained
by induction hardening is higher than it by ordinary
quenching, because of compressive residual stress
generated by the process.
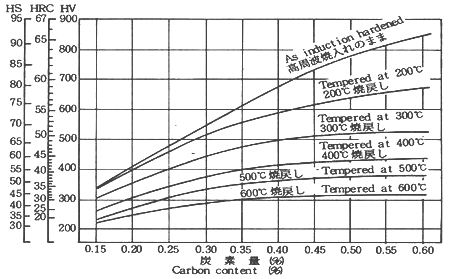
- While maintaining
hardness and residual stress, tempering is to be carried
out in order to prevent deforming, grinding crack
and to improve toughness.
|
 |
|
Carbon
content & quenching hardness
|
 |
 |
|
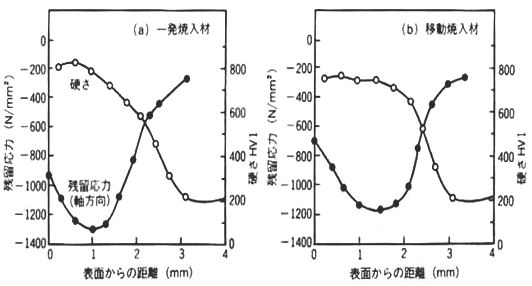
Distribution
of hardness & residual stress
|
Carbon
content & tempered hardness
|
|
|
| INDUCTION
HARDENED DEPTH |
- For controlling
induction hardening, as it is difficult to measure
Austenitizing temperature directly, frequency(penetrate
depth), power density, ampere and voltage, heating
duration are used instead.
- The lower frequency
is applied, the deeper harden depth is obtained.
- There are two
kinds of heating up, those are one shot heating and
progressive heating.
|
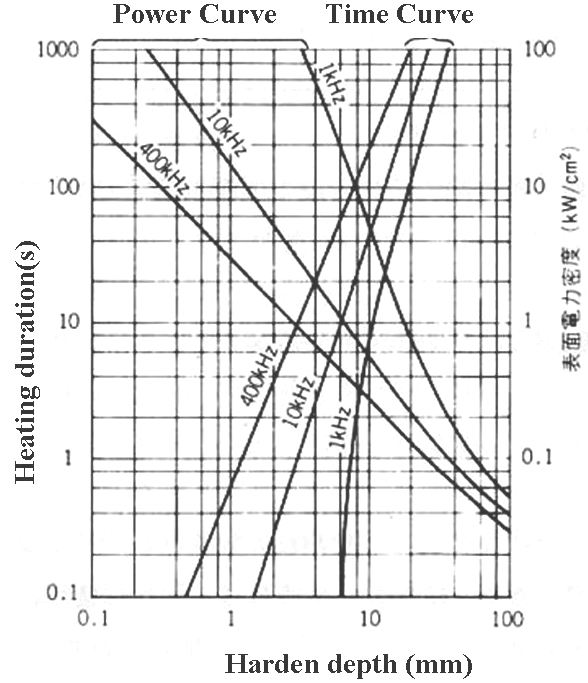 |
| Relationship
between hardened depth and heating duration, power density
and frequency |
|
|
Top
|




